Select Number of BBs below

Introduction to Nash Equilibrium in Short-Stacked Heads-Up Play
In heads-up poker with a 20 big blind (BB) effective stack, players are in a dynamic, high-pressure situation where aggression and precision are critical. Unlike deeper-stacked play, where there is room for postflop maneuvering, a 20BB stack size makes preflop decisions significantly more important, often reducing the game to push or fold scenarios.
The Nash Equilibrium push/fold strategy is a mathematically optimal approach where both players make decisions that neither can exploit. If both players follow Nash equilibrium, no one can improve their expected value (EV) by deviating from the strategy. While real-world adjustments based on opponent tendencies can be beneficial, understanding this unexploitable baseline is crucial for success.
Why Push/Fold at 20BB?
At shallower stack depths, postflop play becomes less relevant because:
- The stack-to-pot ratio (SPR) is low, meaning that postflop decisions often result in all-ins within a few betting rounds.
- Raising small and folding to aggression becomes inefficient, as opponents can easily pressure you with shoves.
- Limping strategies, while viable in some exploitative settings, are not part of a pure Nash push/fold framework.
- Shoving maximizes fold equity, reducing the chance of playing postflop with a marginal hand.
Thus, at 20BB, many hands that might be played passively or raised in deeper-stacked situations are instead shoved all-in preflop to maximize immediate equity and deny opponents profitable decisions.
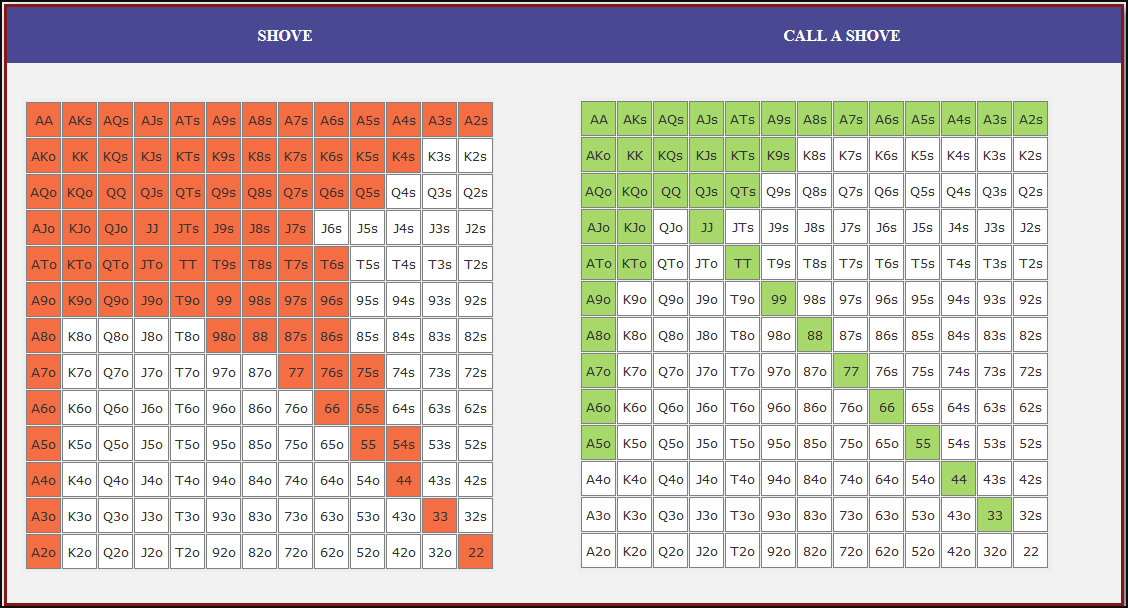
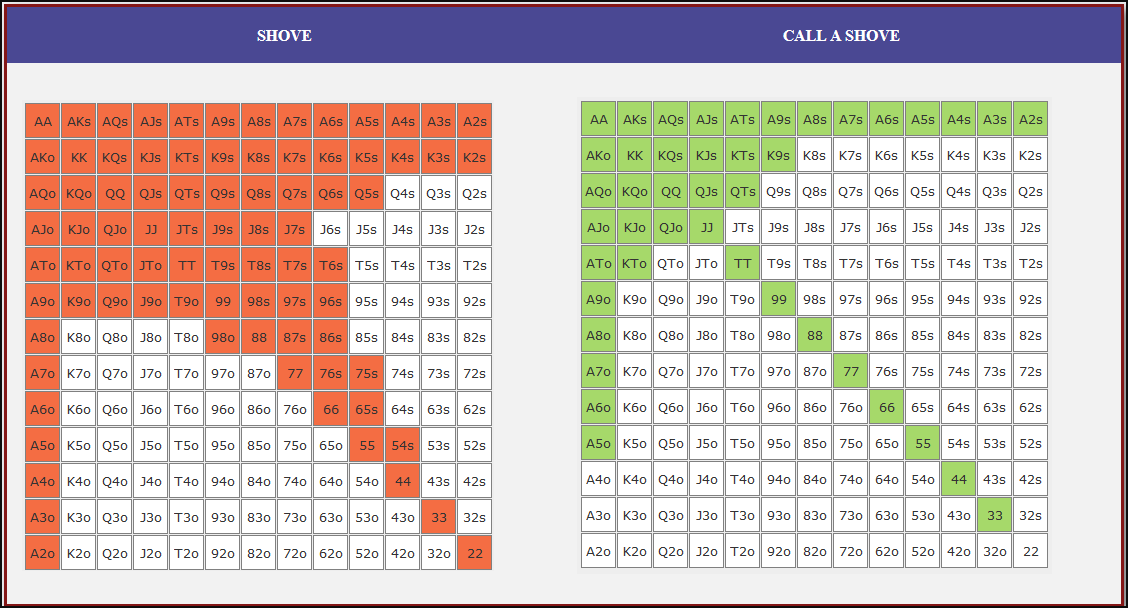
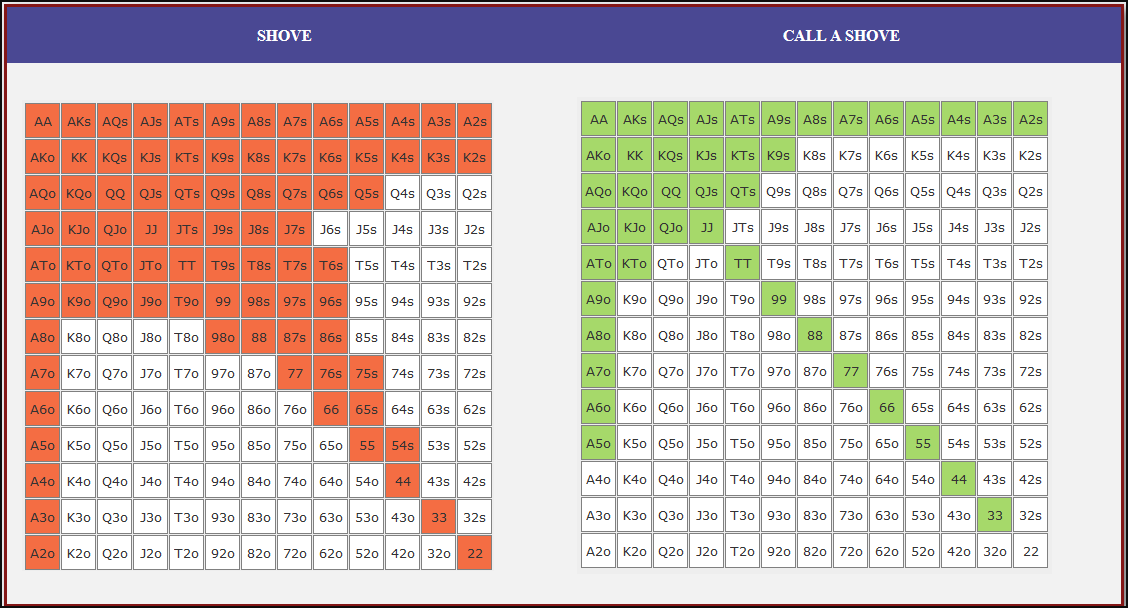
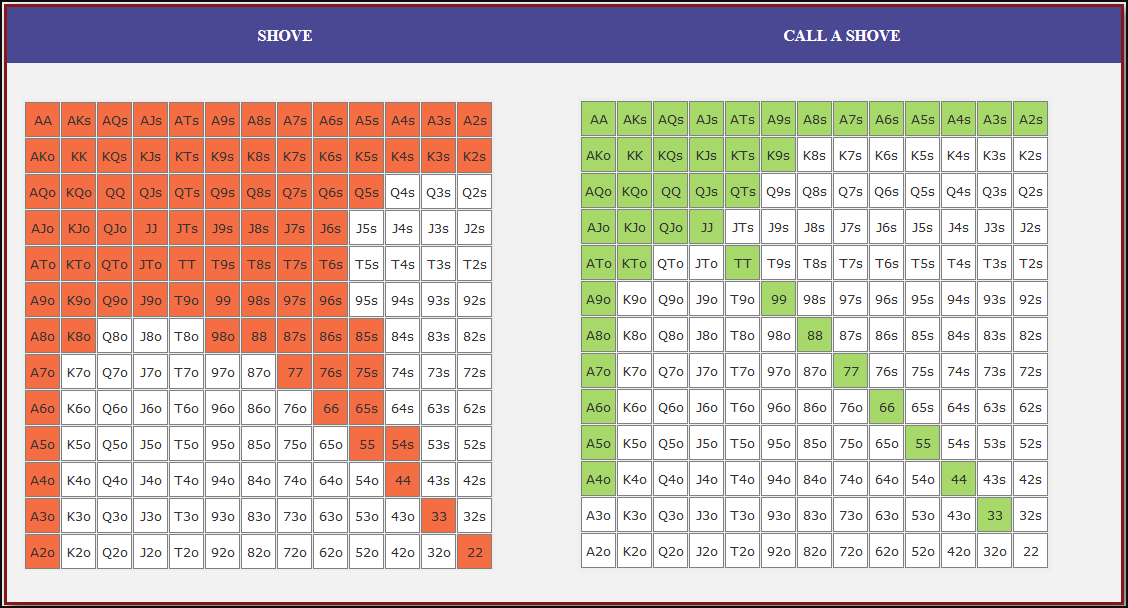
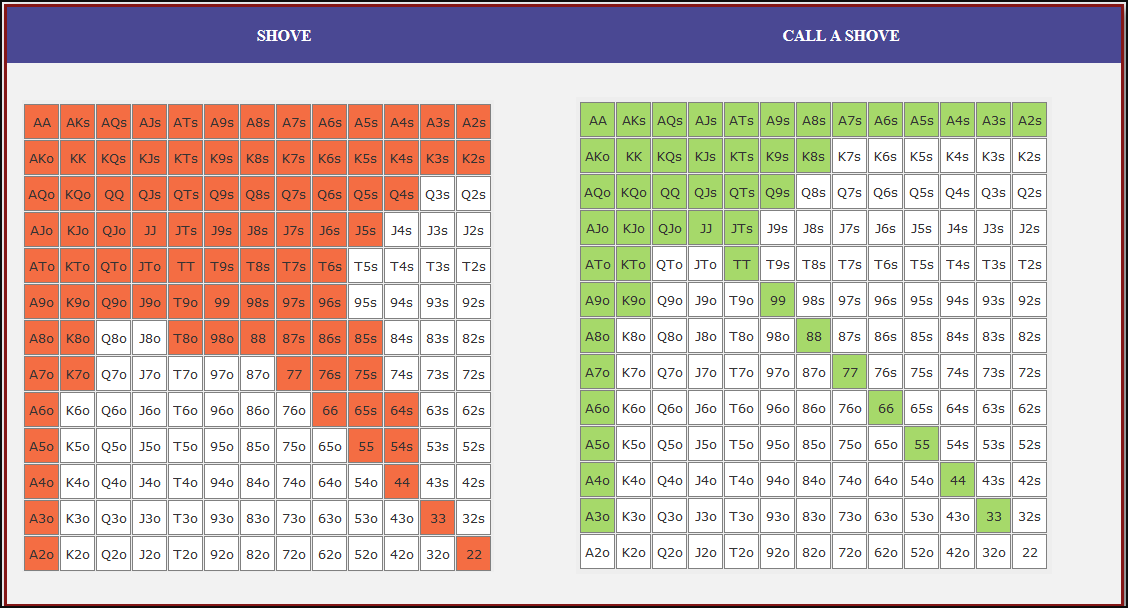
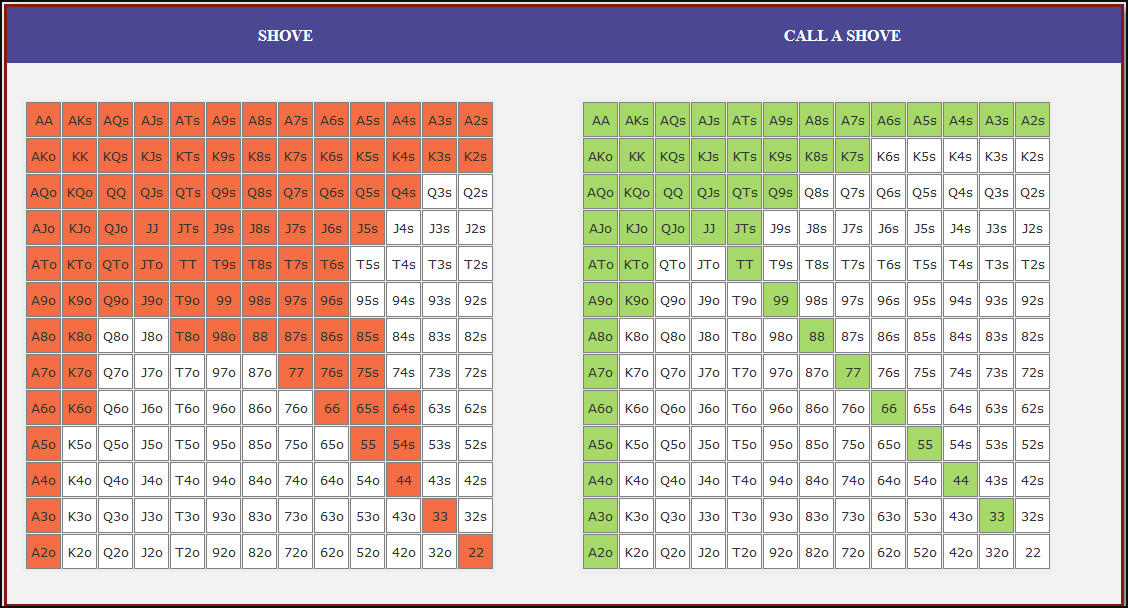
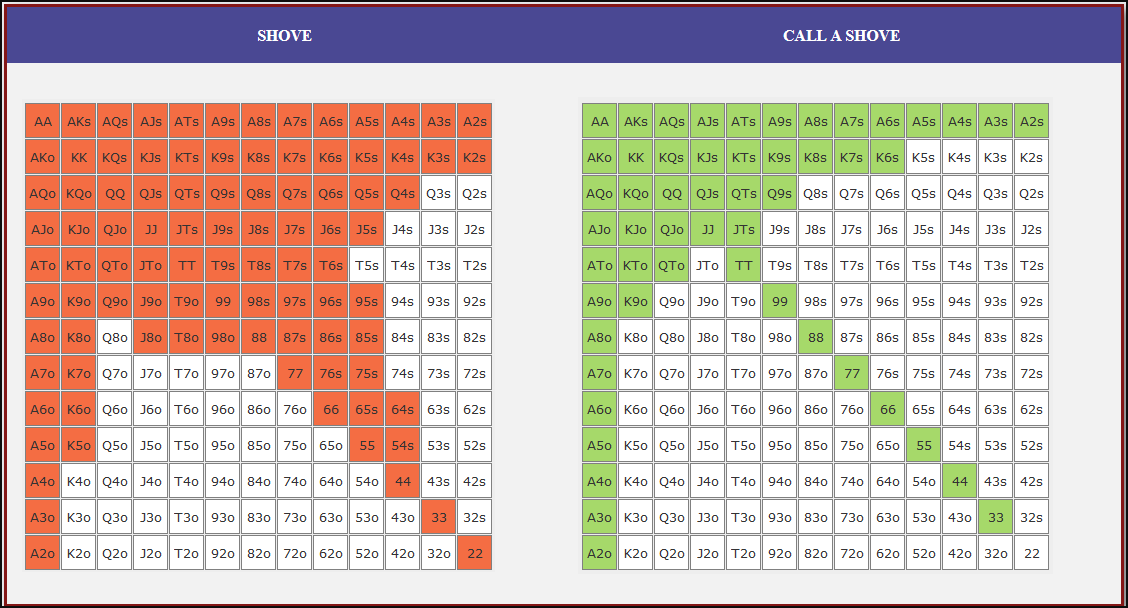
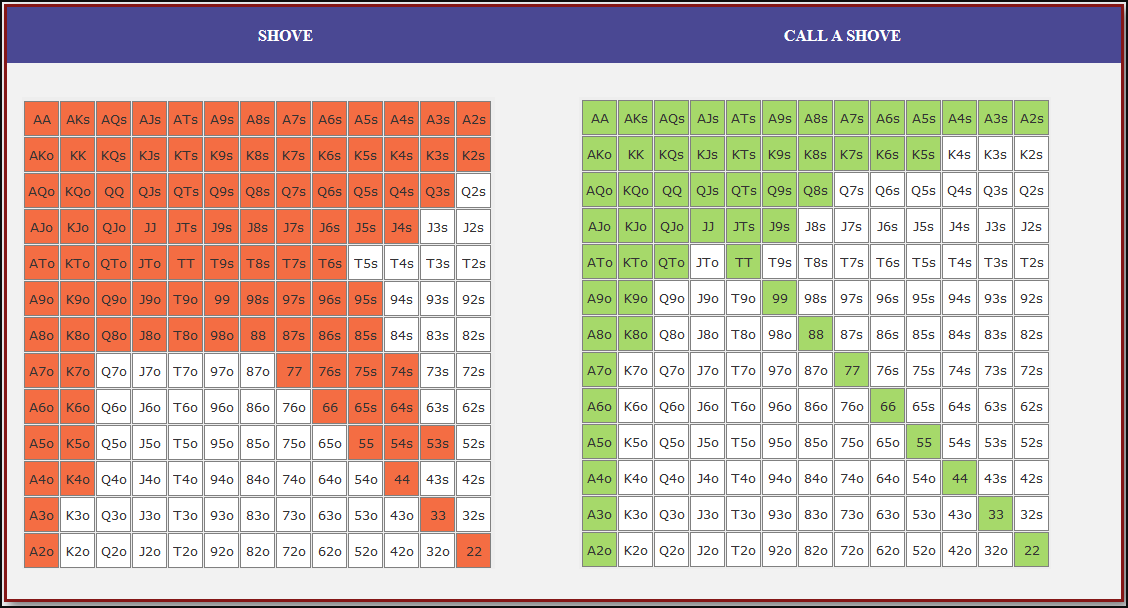
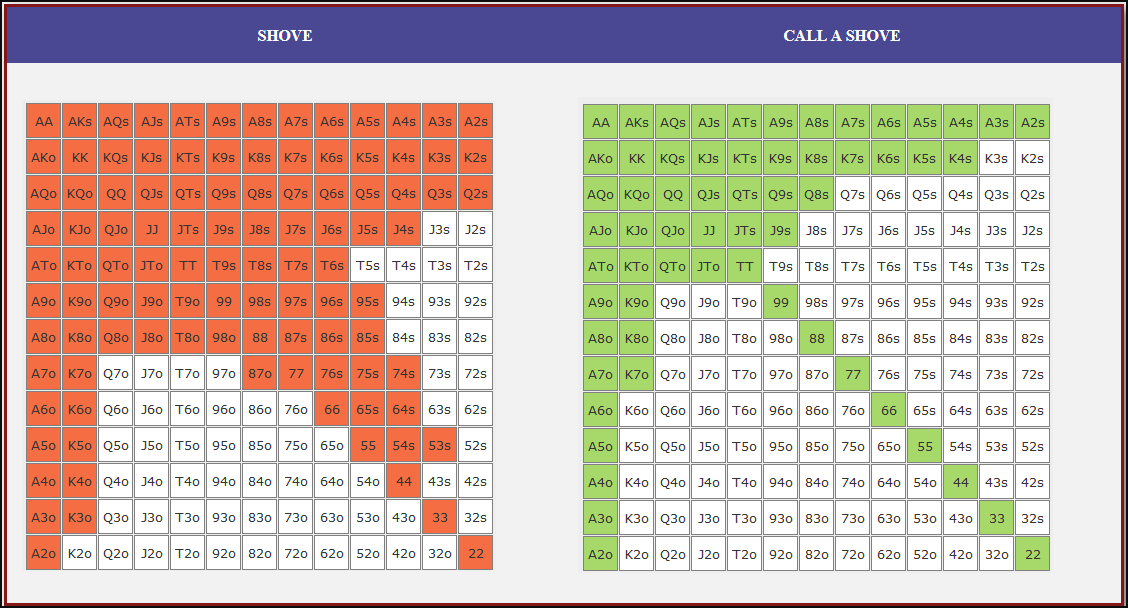
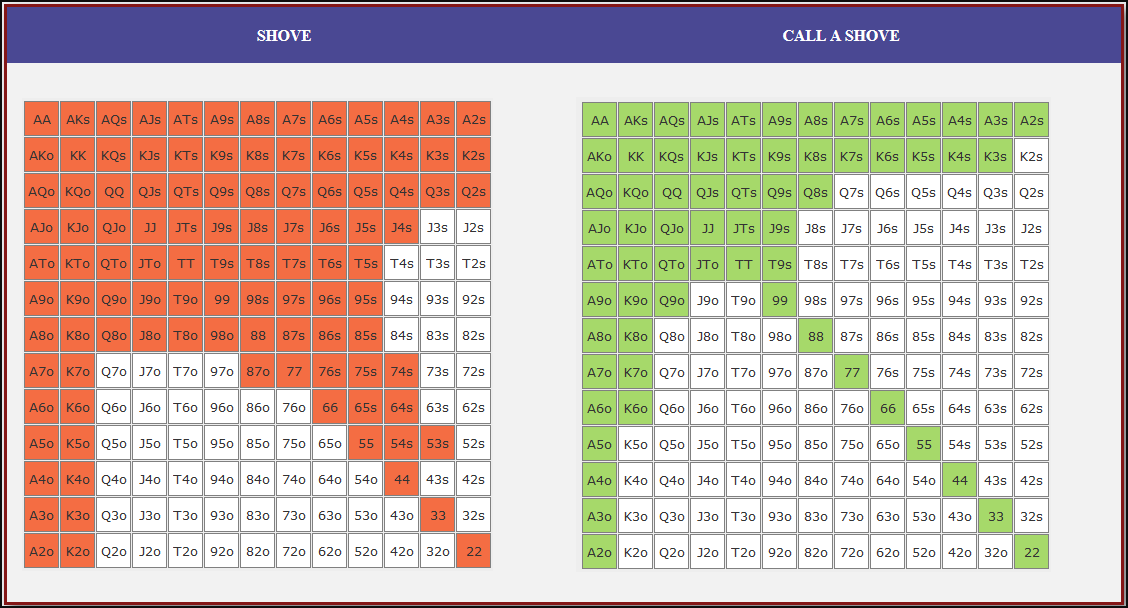
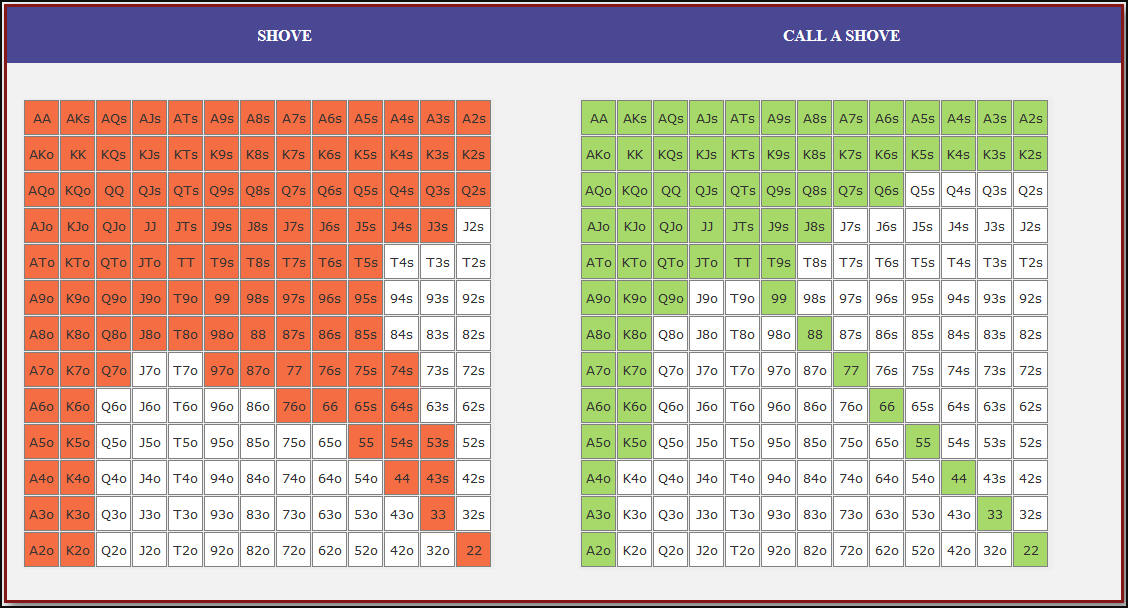
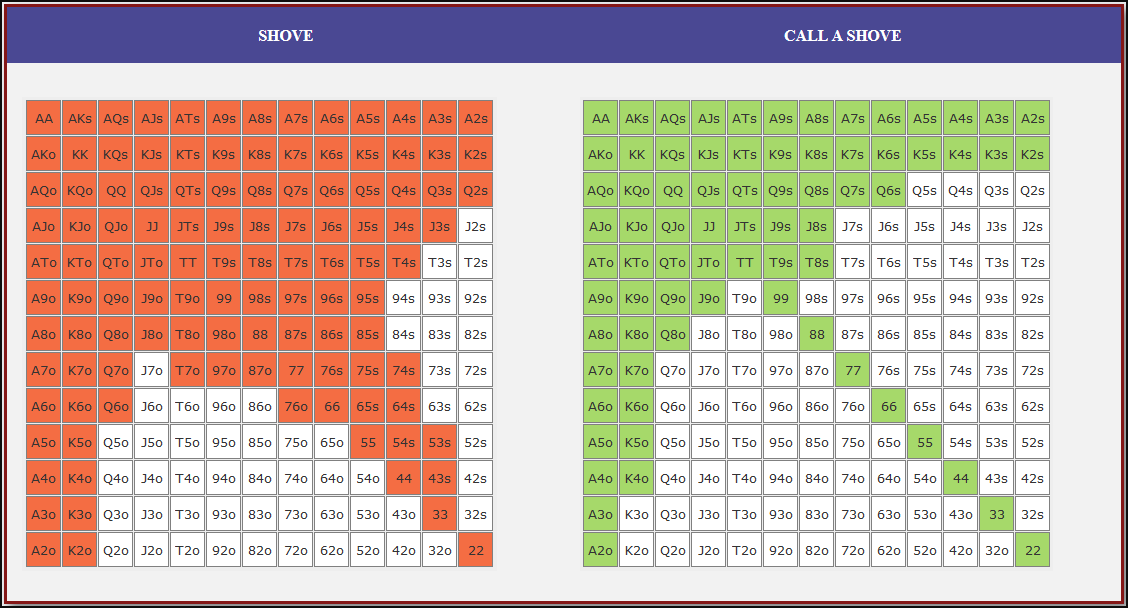
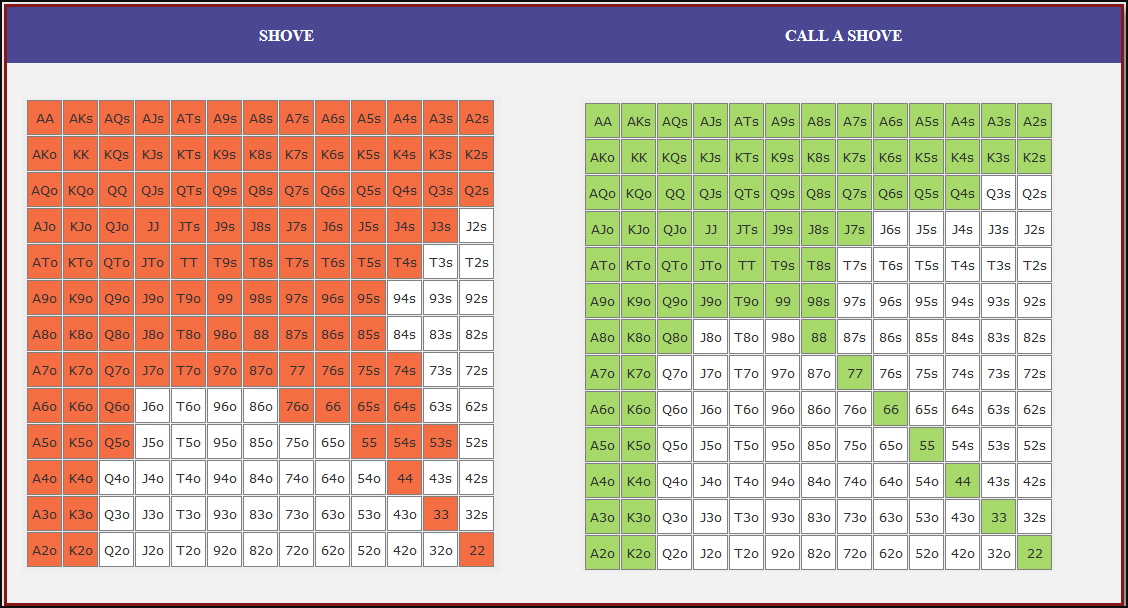
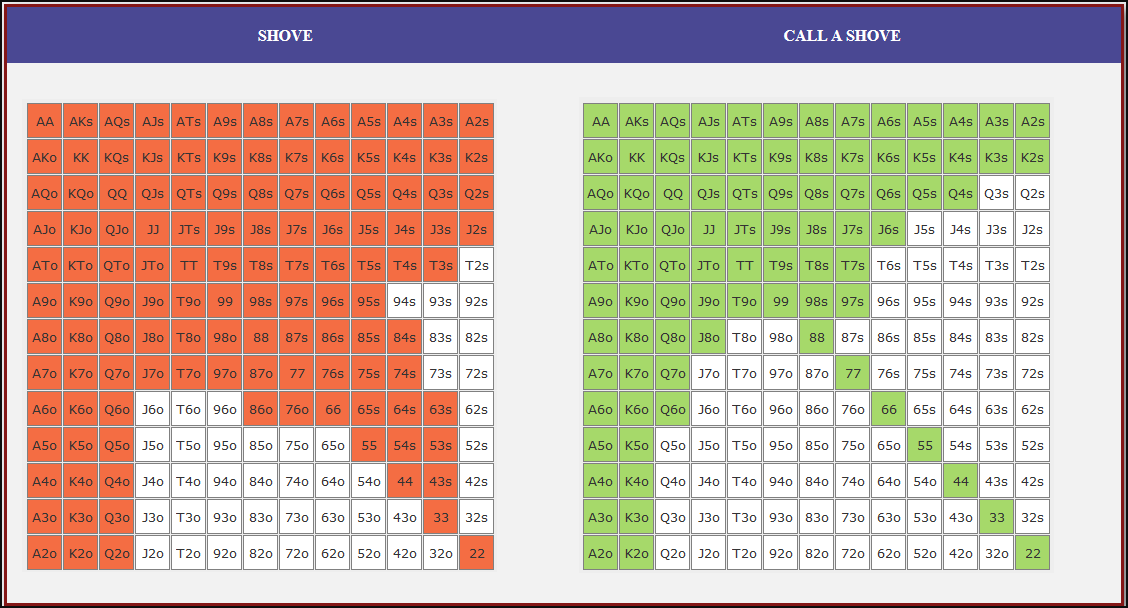
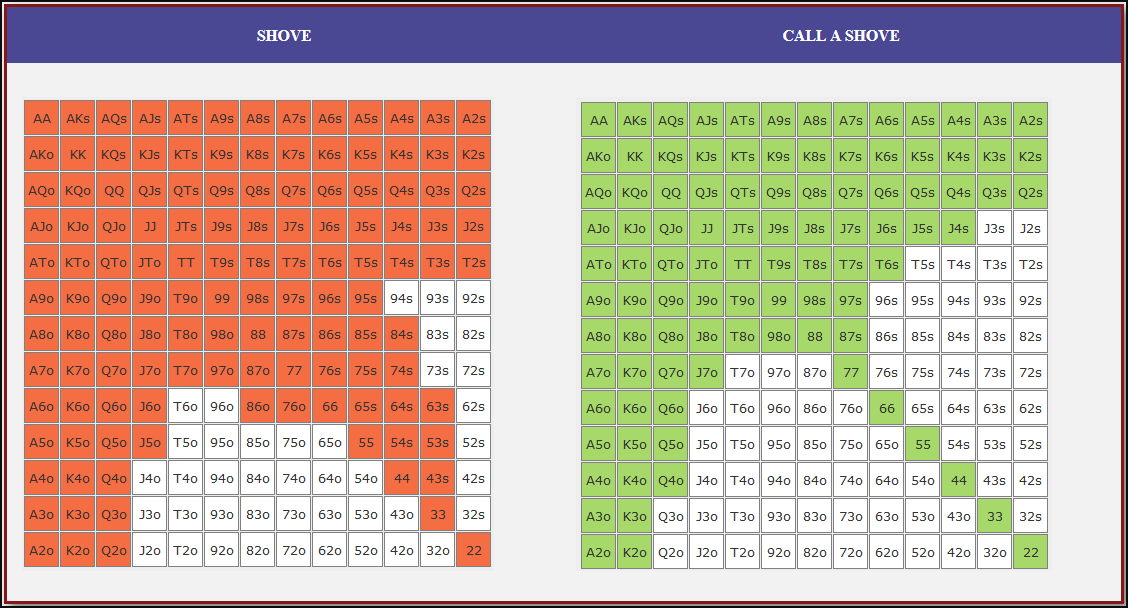
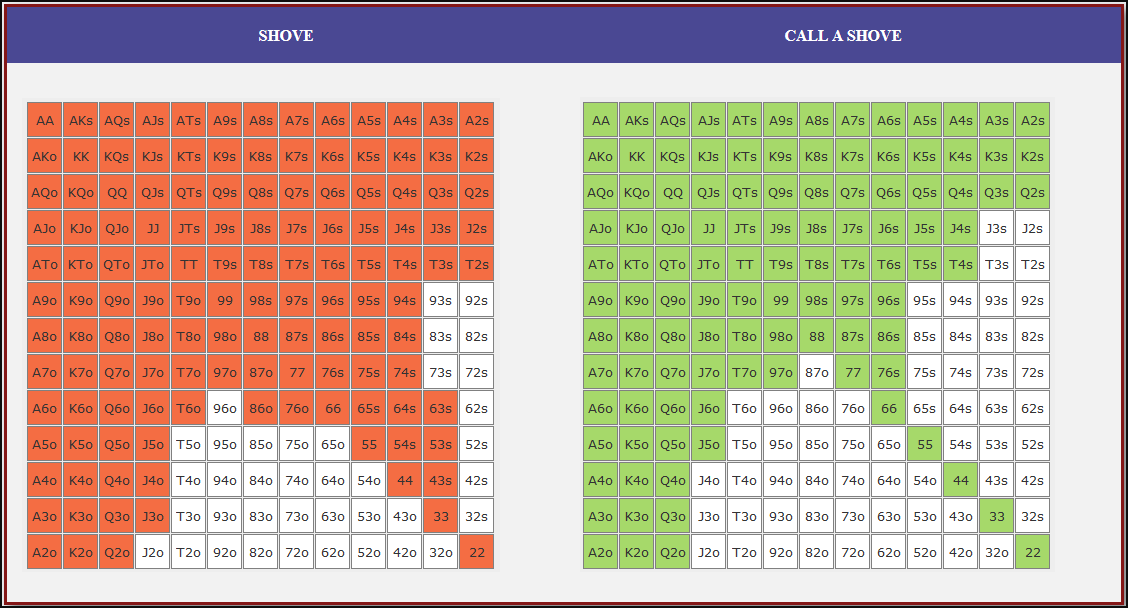
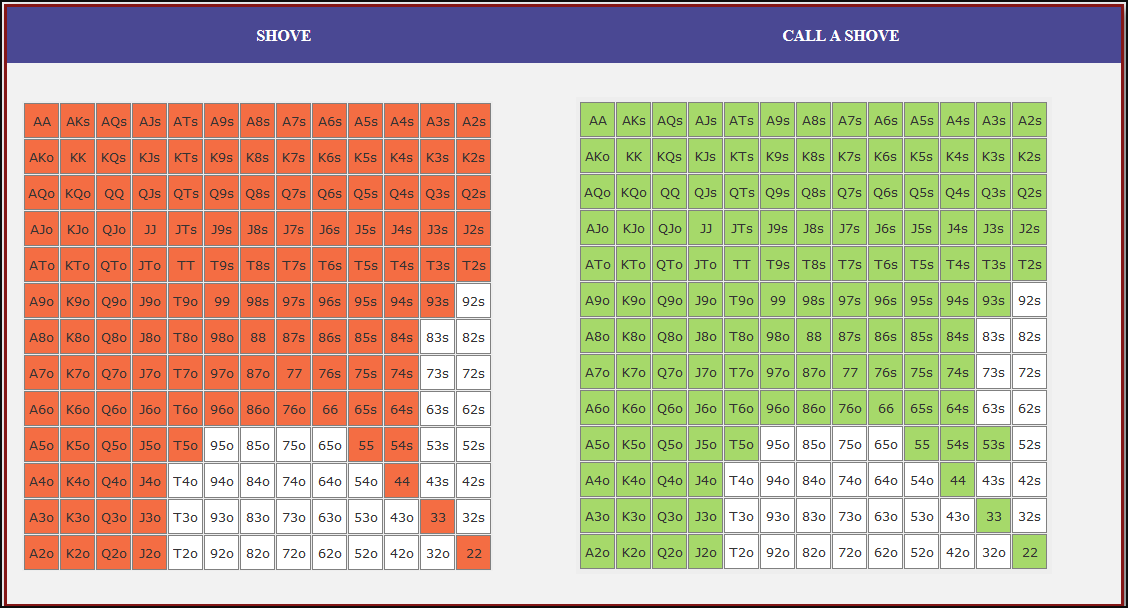
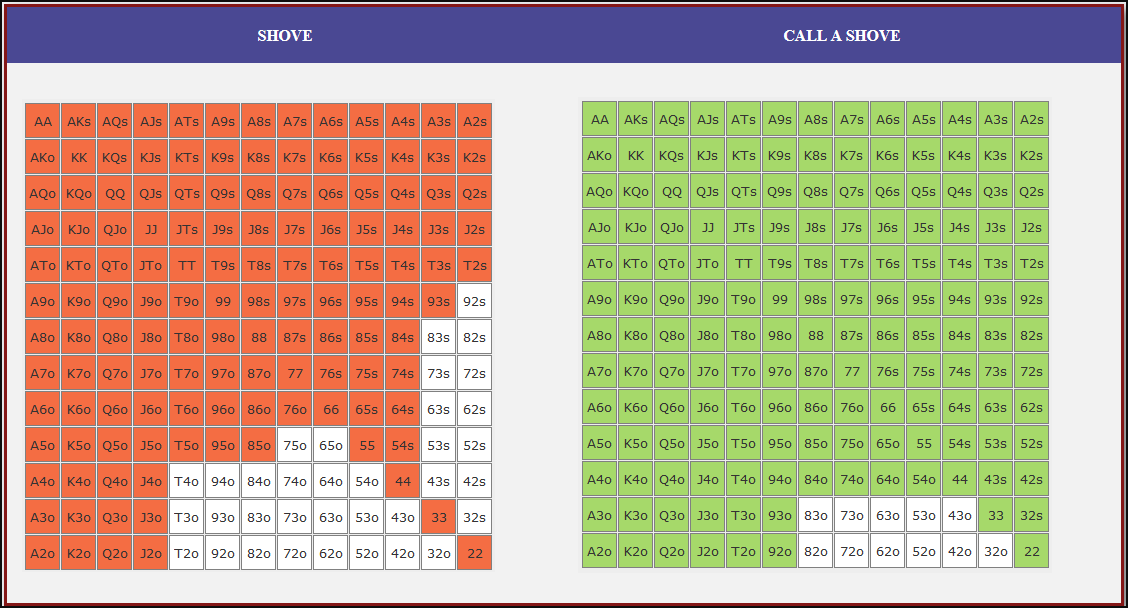
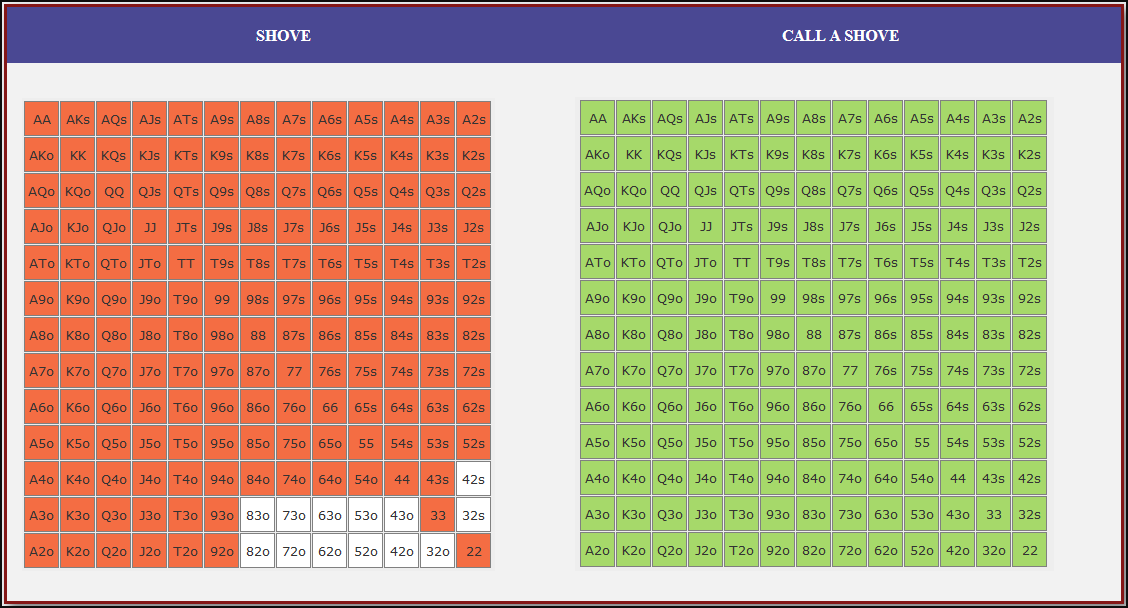
Small Blind (SB) Strategy: When to Shove or Fold
The small blind (SB) is out of position postflop, meaning that it is often correct to apply maximum pressure by shoving all-in rather than making a standard raise. The key factors influencing whether a shove is profitable include:
- Hand strength: Stronger hands naturally benefit from shoving since they retain significant equity when called.
- Opponent’s calling range: If the big blind (BB) is calling too wide, the SB should shove more selectively with stronger hands. If the BB is folding too much, SB should shove a much wider range to exploit this tendency.
- Risk vs. reward: While small raises could keep weaker hands in play, they also invite the risk of being re-shoved on by the BB, putting the SB in a difficult situation.
At 20BB effective, Nash equilibrium suggests that the SB should not shove 100% of hands but rather adopt a balanced strategy, shoving a mix of strong hands for value and weaker hands that still retain fold equity. The SB should avoid shoving hands that have poor equity when called and that lack sufficient fold equity against a Nash BB calling range.
Big Blind (BB) Strategy: When to Call or Fold
The big blind (BB) faces a crucial decision when the SB shoves. Since the BB has already committed one blind, it will be getting a decent price to call, meaning that folding too often can result in a loss of EV. However, calling too wide is also problematic, as it allows the SB to profitably shove an even wider range.
Key factors in the BB’s decision-making include:
- Pot odds vs. hand equity: The BB must compare the price of calling with the equity of the hand versus the SB’s shoving range.
- Domination risk: Certain hands, like weak offsuit broadways or small suited connectors, can be in terrible shape against the SB’s stronger shoving range, making them unprofitable calls despite reasonable raw equity.
- Stack preservation: At 20BB, preserving fold equity for future spots can sometimes be more valuable than making a marginally profitable call.
A perfect Nash equilibrium BB strategy will call with hands that have enough equity against the SB’s range while avoiding hands that are dominated too frequently. If the SB is shoving too aggressively, the BB can widen its calling range to punish this over-aggression. Conversely, if the SB is not shoving wide enough, the BB should tighten up its calling range, ensuring that it only calls with a range that dominates the opponent’s actual shoving hands.
Final Thoughts
The 20BB Nash Equilibrium push/fold strategy is an essential tool for heads-up tournament play and short-stacked cash games, providing a mathematically optimal decision-making framework for all-in or fold situations. While this strategy is unexploitable in a vacuum, true mastery involves understanding how opponents deviate from Nash play and adjusting accordingly.
By refining shoving ranges from the small blind and calling ranges from the big blind, players can maximize their equity, apply pressure efficiently, and make profitable decisions in short-stacked heads-up poker.